Is Milk Good for Keto? Unveiling the Truth About Milk’s Role in the Ketogenic Diet!
Understanding the Ketogenic Diet
If you’re intrigued by the idea of a diet that encourages indulging in high-fat foods, the ketogenic diet might pique your interest. The ketogenic diet, or keto diet for short, has gained popularity for its focus on low-carb, high-fat eating patterns. By drastically reducing carbohydrate intake and replacing it with healthy fats, the body shifts into a metabolic state called ketosis, where it becomes incredibly efficient at burning fat for energy.
One common question that arises in the context of the keto diet is whether milk is suitable for this eating approach. Milk is a staple in many households and is considered a valuable source of nutrients, but its carbohydrate content has sparked a debate among keto enthusiasts. Let’s delve into this topic to unravel the truth about milk’s role in the ketogenic diet.

Nutritional Content of Milk
When it comes to the ketogenic diet, understanding the nutritional content of milk is essential in determining if it aligns with your dietary goals. Let’s delve into the macronutrients and micronutrients present in milk to unravel the truth about its role in the keto lifestyle.
Macronutrients
Milk is rich in macronutrients, including carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. A one-cup serving of whole milk contains around 12 grams of carbohydrates. However, it’s important to note that lactose, the natural sugar found in milk, contributes to the carbohydrate content. For individuals following a strict keto diet, it’s crucial to monitor their carb intake, and they may opt for unsweetened almond or coconut milk, which contains significantly fewer carbs.
Regarding fats, milk contains varying levels depending on the fat content. Whole milk has the highest fat content among commonly consumed varieties, while options like skimmed milk have significantly lower fat content. Proteins are another essential macronutrient present in milk, providing the building blocks for muscle growth and repair.
Micronutrients
In addition to macronutrients, milk is packed with essential vitamins and minerals. It’s an excellent source of calcium, vital for bone health, and contains significant amounts of vitamin D, necessary for calcium absorption. Other micronutrients found in milk include vitamin A, B vitamins, and potassium.
Milk’s micronutrient profile makes it a valuable addition to the diet, contributing to overall nutrient intake. For individuals on a keto diet, the inclusion of milk can provide diverse micronutrients not easily obtained from other sources.
Moreover, research has shown that milk consumption is associated with positive health outcomes, including improved bone health and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease. However, it’s important to opt for unsweetened or unflavored varieties to minimize added sugars and carbohydrates.
Understanding the macronutrients and micronutrients in milk empowers individuals to make informed decisions about its role in their keto journey.
Carbohydrate Content in Milk
One of the key considerations for anyone following a ketogenic diet is the carb content in different types of milk. Let’s delve into the carb content of various milk options and their impact on ketosis.
Whole Milk
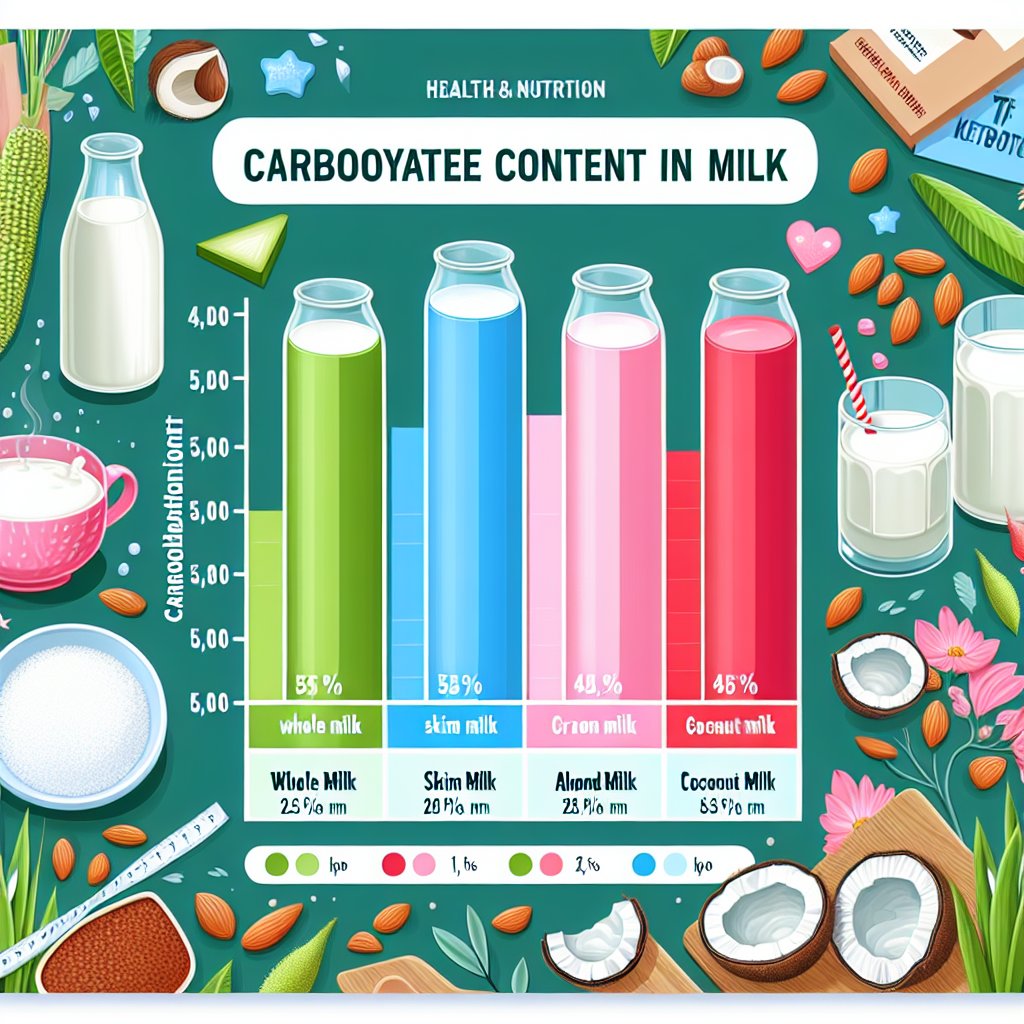
Whole milk is known for its creamy texture and rich flavor. However, it’s important to note that it contains around 12 grams of carbs per one cup (240 ml). For individuals on a strict keto diet aiming for a low daily carb intake, whole milk might not be the most suitable option due to its relatively high carb content.
Skim Milk
Skim milk, often chosen for its lower fat content, contains approximately 11-12 grams of carbs per one cup (240 ml). While it offers a slightly lower carb content than whole milk, it still may not be ideal for those pursuing deep ketosis.
Alternative Milks: Almond and Coconut Milk
Almond milk and coconut milk have gained popularity as low-carb milk alternatives in the keto community. Typically, unsweetened almond milk contains just 1-2 grams of carbs per cup (240 ml), making it a favorable choice for individuals on the ketogenic diet. Coconut milk, on the other hand, contains around 3 grams of carbs per cup (240 ml), which is also relatively low and can be incorporated into a keto meal plan.
Switching from whole or skim milk to almond or coconut milk can significantly reduce your carb intake, supporting your efforts to reach and maintain ketosis.
While considering the carb content in different types of milk is essential, it’s equally important to remember that individual responses to dairy and dairy alternatives can vary. Some people may find that certain milk options have a greater impact on their blood sugar levels and ketone production, affecting their state of ketosis.
Exploring the Fat Content in Milk and Its Role in a Keto Diet
When it comes to the ketogenic diet, a key aspect is the consumption of healthy fats to achieve and maintain ketosis. Many people are often inquisitive about whether milk can be a part of their keto lifestyle, considering its fat content. Let’s delve into the fat content of milk and its relevance in a keto diet.
Firstly, it’s crucial to understand that the fat content in milk can vary depending on the type of milk. Whole milk, for example, contains about 8g of fat per one cup serving. Additionally, milk also contains various fatty acids, including medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which are known for their potential to enhance ketone production in the body, aiding in the process of ketosis.
Research has shown that consuming dairy fats, such as those found in milk, can have favorable effects on weight management and metabolic health. A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that dairy fat intake was not associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, but rather had a neutral effect on heart health.
Furthermore, the fat in milk plays a crucial role in helping the body absorb fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamin D, which is essential for bone health and overall well-being. Therefore, incorporating milk with a higher fat content into your keto diet may contribute to a more balanced micronutrient intake, supporting your body’s nutritional needs while on the ketogenic journey.
Considering these factors, it’s evident that the fat content in milk can indeed align with the principles of a keto diet, emphasizing the significance of consuming healthy fats for ketosis while also reaping potential health benefits associated with dairy fat consumption.
Proteins and Other Nutrients in Milk: A Powerhouse for Ketogenic Diet
When it comes to the ketogenic diet, the spotlight often falls on fats and carbohydrates. However, proteins also play a crucial role in this low-carb, high-fat lifestyle. And one of the richest sources of high-quality protein is milk. Let’s take a deep dive into the protein content in milk and its significance for muscle growth and overall health, as well as explore other essential nutrients present in this versatile dairy product.
Protein Power: Fueling Muscle Growth and Repair
Milk contains two main types of protein: casein and whey. These proteins are considered to be of high biological value, meaning they provide all essential amino acids in a highly digestible form. In fact, whey protein is a complete protein, containing all nine essential amino acids necessary for optimal health. These amino acids are the building blocks of muscle tissue and are essential for muscle growth and repair.
For individuals following a ketogenic diet, consuming adequate protein is crucial for preserving lean muscle mass while burning fat for energy. The amino acids derived from milk protein can help support muscle recovery after exercise and provide the necessary building blocks to maintain muscle strength and function.
Other Essential Nutrients in Milk
Aside from its protein content, milk is also rich in other essential nutrients that are valuable for overall health. One of the most notable nutrients found in milk is calcium, which is crucial for maintaining strong bones and teeth. Additionally, milk is fortified with vitamin D, a nutrient that works in tandem with calcium to support bone health and plays a role in immune function and mood regulation.
Furthermore, milk is a good source of B vitamins, including riboflavin, vitamin B12, and pantothenic acid, which are involved in energy metabolism and the maintenance of healthy skin, eyes, and hair. These nutrients are essential for overall wellness and can complement the nutritional needs of individuals following a ketogenic diet.
Incorporating milk into the ketogenic diet can provide a valuable array of nutrients, including high-quality proteins, essential vitamins, and minerals, all of which contribute to overall health and well-being.
With its protein power and array of essential nutrients, milk is indeed a standout player that can be a beneficial addition to a well-rounded ketogenic diet.

Impact of Milk on Ketosis
One of the most discussed topics in the keto community is the impact of milk consumption on ketosis. As a dairy product, milk contains lactose, which is a type of sugar. Therefore, it’s essential to analyze how milk consumption affects ketosis and understand the potential risks of including milk in a ketogenic diet.
Milk and Ketosis
When it comes to ketosis, the goal is to keep your body in a state where it burns fat for energy instead of relying on carbohydrates. The consumption of milk, particularly high-carb varieties, can potentially interfere with this state. For instance, an 8-ounce glass of regular cow’s milk contains around 12 grams of net carbs, which can significantly impact ketosis if consumed in large quantities.
However, it’s important to note that there are lower-carb milk alternatives such as unsweetened almond milk and coconut milk. These options typically contain fewer net carbs and can be incorporated into a ketogenic diet in moderation.
Potential Risks of Consuming Milk on a Ketogenic Diet
While milk can be a valuable source of nutrients such as calcium and vitamin D, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential risks associated with consuming milk on a ketogenic diet. One risk is the impact on blood sugar levels due to the lactose content in milk. Lactose can cause an increase in blood sugar, potentially leading to a decrease in ketone production and hindering the process of ketosis.
Additionally, some individuals may experience digestive issues such as bloating, gas, or discomfort when consuming milk, especially if they are sensitive to lactose. These issues can not only be uncomfortable but may also disrupt the overall well-being of individuals following a ketogenic lifestyle.
Moreover, the calorie content of milk should also be taken into consideration. Consuming high-calorie beverages like whole milk in large quantities can contribute to an overall increase in calorie intake, which may hinder weight loss efforts, a common goal for individuals following the ketogenic diet.
On the other hand, choosing lower-calorie and lower-carb alternatives such as unsweetened almond milk or coconut milk can mitigate these risks while still providing essential nutrients and adding variety to the diet.
In conclusion, while milk can be a contentious topic in the keto community, it’s important to make informed choices based on individual health goals and dietary preferences. Opting for lower-carb and lower-calorie milk alternatives may allow individuals to enjoy the benefits of milk while minimizing the potential risks and maintaining ketosis.
Alternatives to Milk on Keto
So, you’ve decided to embrace the ketogenic lifestyle, and you’re wondering if milk is a good fit for your new way of eating. While cow’s milk is not ideal due to its higher carb content, fear not! There are plenty of keto-friendly milk alternatives to fulfill your dairy cravings. Let’s explore some popular options along with their nutritional profiles.
Almond Milk
Almond milk is a fantastic low-carb alternative to traditional cow’s milk. It’s made from ground almonds and water, making it naturally low in carbohydrates and high in healthy fats. A one-cup serving of unsweetened almond milk contains only 1-2 grams of net carbs, making it an excellent choice for those following a ketogenic diet. Additionally, almond milk is fortified with vitamins A, D, and E, providing essential nutrients for overall health.
Coconut Milk
Another great dairy-free option for keto dieters is coconut milk. This rich and creamy milk is derived from the flesh of coconuts and has a high-fat content, making it a perfect fit for the keto lifestyle. A one-cup serving of canned coconut milk contains around 3 grams of net carbs. It’s also a good source of medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which can be easily converted into ketones, providing a quick source of energy for those in ketosis.
Hemp Milk
Hemp milk is a lesser-known but equally valuable alternative to cow’s milk. Made from hulled hemp seeds and water, hemp milk is rich in omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, making it a heart-healthy option. With approximately 1-2 grams of net carbs per cup, hemp milk is a low-carb beverage that can easily fit into your keto meal plan. It also contains all nine essential amino acids, making it a complete protein source, which is beneficial for muscle health and overall well-being.
When incorporating these keto-friendly milk alternatives into your diet, always opt for unsweetened varieties to minimize your sugar intake. Whether you prefer the nutty taste of almond milk, the creamy texture of coconut milk, or the nutritional benefits of hemp milk, you can enjoy these delicious alternatives while staying true to your ketogenic goals.
Is Milk Good for Keto? Unveiling the Truth About Milk’s Role in the Ketogenic Diet!
Summarizing the Key Points Regarding Milk Consumption on a Keto Diet
Hey there, keto warriors! We’ve dived deep into the world of milk and its role in the ketogenic diet. Let’s sum up the key takeaways:
-
Carb Content: Cow’s milk is relatively high in carbohydrates, with around 12g per one cup (240ml). This can quickly add up and potentially kick you out of ketosis.
-
Protein and Fat: Milk contains both protein and fat, which are essential on a keto diet. However, the protein and fat content in whole milk may not align with the high-fat, moderate-protein keto principles.
-
Calcium and Other Nutrients: Milk is a natural source of calcium and other essential nutrients like vitamin D, vitamin B12, and potassium. These nutrients are crucial for overall health, but there are other keto-friendly sources for these nutrients.
-
Lactose Sensitivity: Many individuals are lactose intolerant and may experience bloating, gas, or other digestive issues when consuming milk.
-
Keto-Friendly Alternatives: Fortunately, there are several keto-friendly milk alternatives such as almond milk, coconut milk, and macadamia milk. These options are lower in carbs and can be incorporated into a ketogenic lifestyle.
Recommendations for Individuals Following a Ketogenic Lifestyle
Now that we’ve unpacked the facts, it’s time for some practical advice for all you keto enthusiasts:
-
Choose Unsweetened Varieties: When opting for milk or milk alternatives, always go for unsweetened versions to avoid added sugars and unnecessary carbs.
-
Watch Your Portions: If you decide to include milk in your keto regimen, pay attention to your portion sizes. Smaller quantities like a splash in your coffee or tea can help manage carb intake.
-
Experiment with Alternatives: Explore the world of keto-friendly milk substitutes. Try almond milk in your smoothies or coconut milk in your curries. You might find a new favorite!
-
Prioritize Nutrient-Dense Foods: While milk does offer some essential nutrients, consider obtaining these from other sources such as leafy greens, nuts, and seeds. This ensures you’re getting a broader spectrum of nutrients without the carb load.
-
Listen to Your Body: If you notice any adverse effects after consuming milk, consider eliminating it from your diet and focusing on alternative sources of nutrition.
In conclusion, the role of milk in the ketogenic diet is nuanced. While it can provide essential nutrients, its carb content may not align with the keto principles for some individuals. Ultimately, it boils down to personalized choices and considering how milk fits into your overall daily carb allowance. So, weigh your options, experiment, and find what works best for your body and your keto journey. Cheers to informed decision-making on this dairy dilemma!


